- They are solid at room temperature, similar to other hot-melt adhesives that are thermoplastic polymers, such as ethylene vinylacetate (EVA), polyalphaolefin (PAO), polyester and polyamide.
- The temperature for application as a melt ranges from 85°C to 140°C (185°F to 284°F), which is less than that for typical thermoplastic hot melt products. The viscosity at the application temperature can be designed in a range from 2,000 to 60,000 cPs depending on the specific requirements.
- HMPUR adhesives are being produced with open times varying from 10 seconds to 10 minutes to match application requirements.
- The unique property that gives HMPUR adhesives their performance advantage compared to thermoplastic hot melts is that they cure to a thermoset material that resists melting. This curing process is the reaction with moisture found in the air or in typical substrates to produce a strong, tough, temperature-resistant adhesive.
The advantages of HMPUR adhesives result from the properties that were described above. Some of these advantages are:
- The cured adhesive has excellent temperature and environmental resistance. Many of the HMPUR adhesives can withstand exposure to temperatures from -40°F to +200°F while maintaining strong bonds.
- Minimal fixturing is needed due to the controlled set time and rapid development of green strength that can be designed into these products. They are typically applied by roll coating, slot-die coating, gravure printing, screen printing or spray coating (swirl or fiberized) and then briefly nipped or pressed to provide a bond with handling strength. Final cure and ultimate strength are achieved in a few hours to a few days depending on the adhesive, substrate and conditions in the plant.
- HMPUR adhesives can be designed and developed with widely varying properties for specific applications. How this is done and some of these applications are described later in this article.
- HMPUR adhesives are 100% solids and therefore have no volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and do not require drying ovens. This eliminates many of the environmental issues associated with solvent-based adhesives and the energy requirements for drying water-based and solvent-based products.
How Specific Properties are Incorporated into HMPUR Adhesives
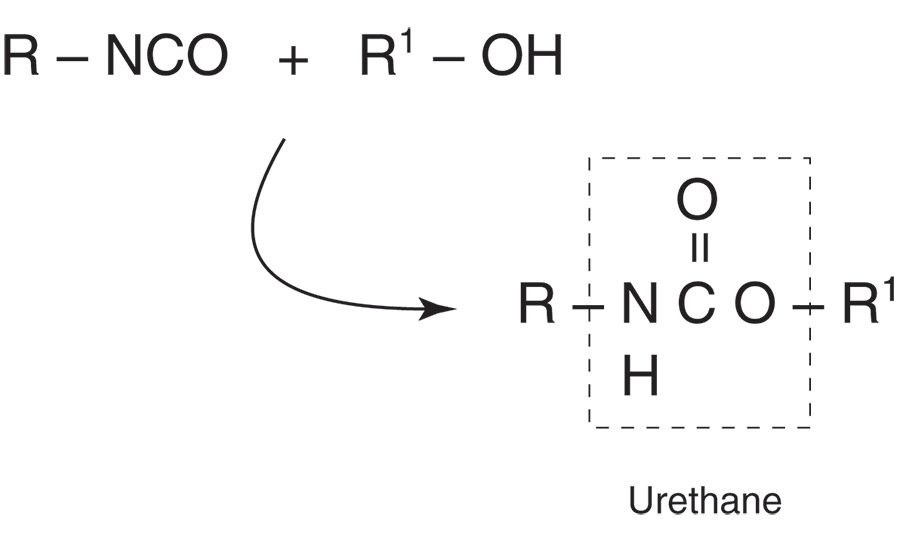
HMPUR adhesives are manufactured by reacting mixtures of polyols with an excess of diisocyanate. The reaction of an isocyanate group (-NCO) with an alcohol group (-OH) produces the urethane group, as shown in Figure 1. The fact that there are excess diisocyanates present means that the molecular weight of the resulting product is not too high and that the HMPUR product will have a controlled melt viscosity.
These adhesives are then transferred from the reactor into the container package as a melt. The container is sealed to prevent exposure to moist air while the adhesive solidifies on cooling. Typical containers are drums (400 lb), pails (40 lb), slugs (4.4 lb) and cartridges (0.6 lb).
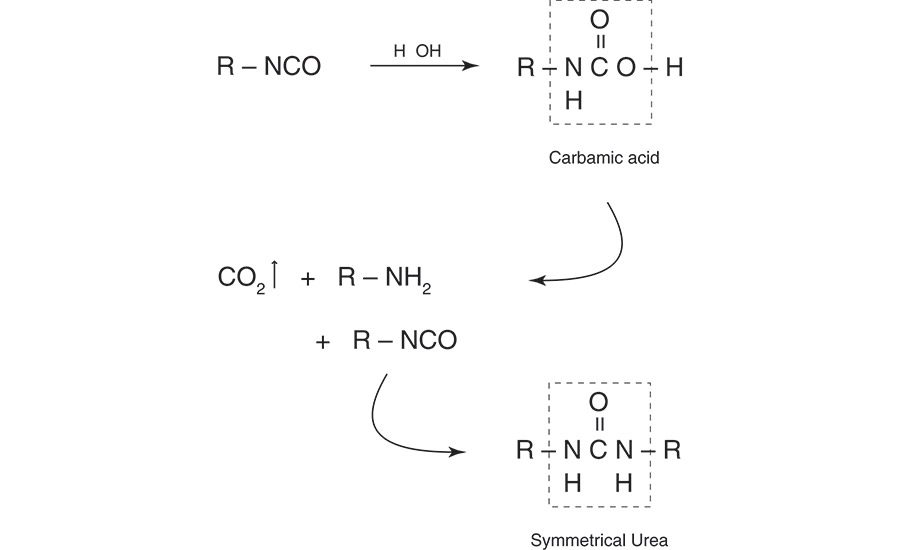
The adhesive is melted using a specifically designed premelter and then applied to the article to be bonded. During the next several hours or days after application, the reaction described in Figure 2 takes place. This reaction of isocyanate with water forms the highly stable polyurea structure that gives the cured HMPUR its temperature and environmental performance. The polyurea structure effectively crosslinks the adhesive to prevent its remelting or dissolving as can occur with standard thermoplastic hot-melt adhesives.
Specific properties required for varying applications are built into the adhesive by the use of a variety of polyols, isocyanates and additives. Polyols are used to vary the open time, set time and ability to wet effectively various surfaces to produce effective bonds. Some typical polyols used are:
- Polyesters, which can be crystalline or amorphous. The crystalline polyols can be used to give short set times and rapid green-strength development. Amorphous polyesters can improve adhesion to specific substrates and increase open time, if required.
- Polyethers, which are low-Tg, amorphous liquids. These help lengthen open time, reduce viscosity and provide good low-temperature flexibility.
- Vinyl-polymerized polyols, which are typically high-molecular-weight, glassy solids. These materials can assist in building green strength and tack while maintaining extended open times.
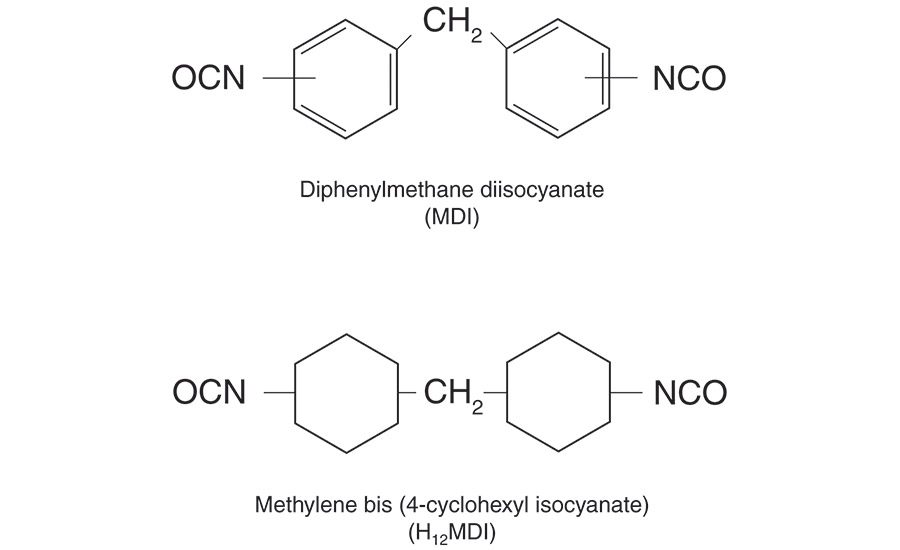
A mixture of polyols to give the desired performance is reacted with an excess of a diisocyanate (Figure 3). Methylene diphenylisocyanate (MDI) is used for most HMPUR adhesives. It has a highly reactive isocyanate group and has a relatively low vapor pressure. Since polyurethanes made with MDI tend to yellow when exposed to sunlight, we also use HMDI (hydrogenated MDI), which resists yellowing very effectively. It tends to be much slower reacting, so we have developed and patented a process to effectively speed its reaction and make it useful for HMPUR applications.
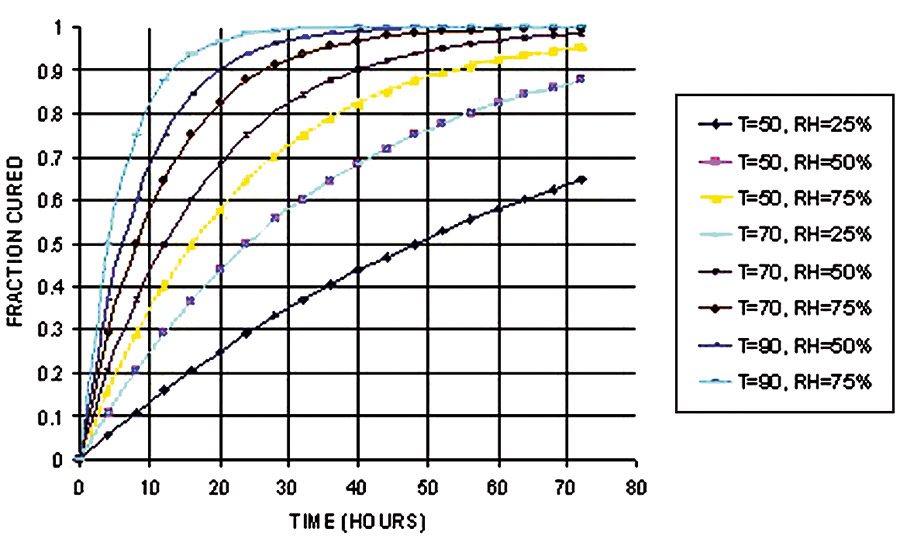
The curing rate of the typical HMPUR adhesives is shown in Figure 4. As you can see, the rate is dependent on both the moisture present, as well as the temperature.
Fire-Rated Laminated Panels
There has been a recent new requirement on construction panels and steel doors to pass a UL 10C fire rating. This is a positive-pressure fire test, which is shown in Figure 5. There is a gas burner inside a brick wall with openings where the panels or doors are placed. The gas flame at a positive pressure is directed at the test pieces. The requirement is that there are no flames issuing from the outside of the test panel for a specified time.
The panels are typically a laminated construction with steel outer skins laminated to 1.5-in.-thick cores. The cores can be honeycomb paper, expanded polystyrene (EPS) foam, polyurethane foam or mineral board. The adhesive is coated on the core with a double-sided roll coater. This adhesive-coated core is then bonded to the steel skins. The edges are typically closed with steel rails, which have the appropriate attachments for hinges, locks, etc.
After assembly, the parts are allowed to cure for a few days and then fire tested. Panels made with earlier versions of the HMPUR adhesive did not pass the UL 10C fire test. Flames were observed on the outside of the test panels from the burning adhesive. New HMPUR adhesives using fire-retardant materials have been recently developed that allow panels to pass this test. Two new specifically designed products, Ever-Lock® 2U232 and 2U236 adhesives, have been introduced that work effectively for our customers in this application. A patent is being applied for on these products.
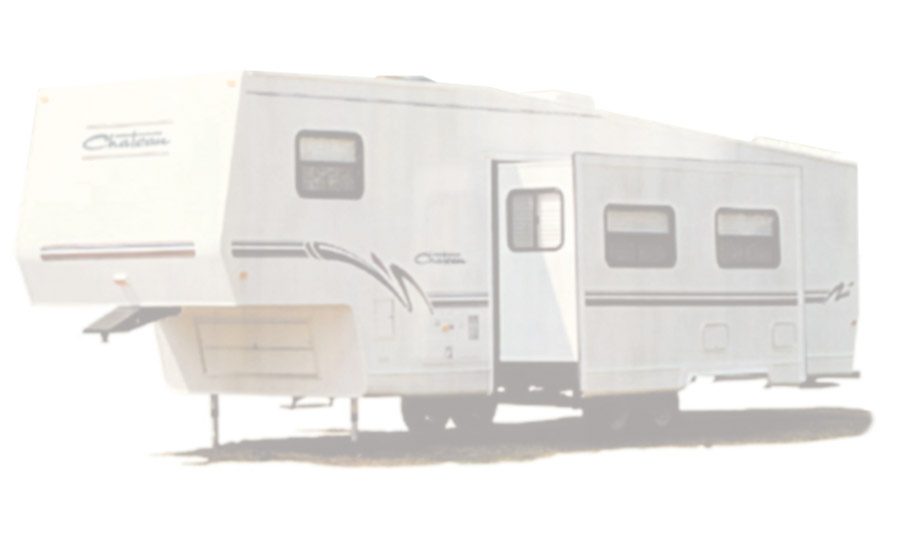
Recreational Vehicles–Motor Homes and Towables
Recreational vehicle side walls are a major application for HMPUR adhesives. The requirements for this application are very demanding. RVs are exposed to a range of environments from cold Northern winters at -40°F to the heat of Arizona summers with the sun beating down on dark sections of side walls to produce 160°F.
The typical construction of the RV side wall is a multilayer lamination using HMPUR adhesives. The layers are:
1. A sheet of fiberglass-reinforced plastic
2, 3. Two layers of lauan plywood
4. A sheet of EPS foam
5. An interior-finish board often with decorative paper
The dimensions of the side walls are as much as 40-ft long by 9-ft high. The ambient temperature during the side-wall manufacture can vary from 60°F to 105°F from winter to summer. The large dimensions of the RV means that long open times, up to three to eight minutes, can be required for the lamination. Also, excellent creep resistance of the adhesive is required to maintain good bonds between stiff and somewhat warped lauan panels.
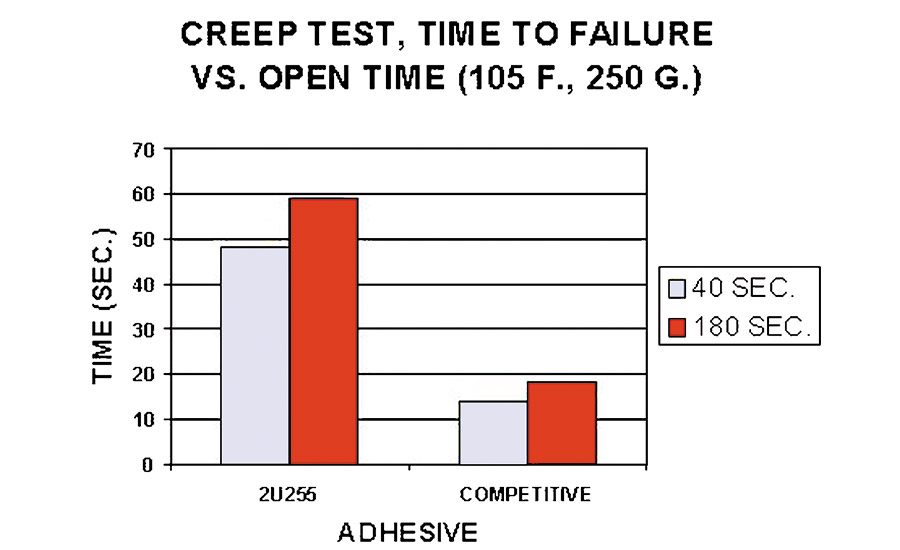
Reichhold offers two new, fully reactive HMPUR adhesives1 to address the requirements of bonding RV side walls. Ever-Lock® 2U255 adhesive provides a long open time and yet a high level of creep resistance at relatively high plant temperatures of 105°F. This would correspond to typical summertime operations in many assembly plants.
Figure 6 graphs the resistance to creep of this product vs. a typical competitive HMPUR adhesive. As can be seen from the graph, the Ever-Lock 2U255 is much more resistant to creep and will maintain a tighter bond under these conditions.
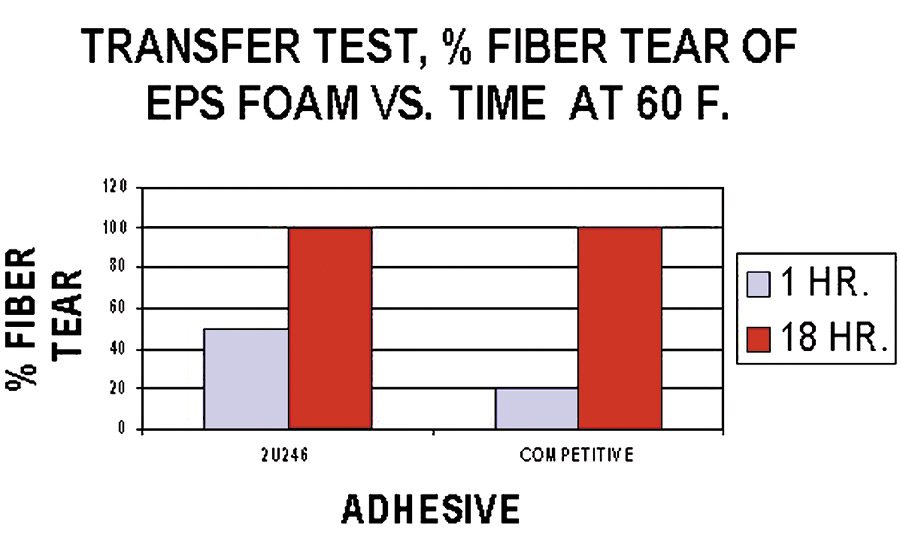
In contrast, at a low application temperature, it is necessary to have a soft, low-Tg adhesive to give good transfer at the extended open time required for RV side-wall assembly. Ever-Lock® 2U246 adhesive satisfies these application requirements. It demonstrates its very effective performance at a substrate temperature of 60°F by rapidly developing sufficient transfer and strength to give good fiber tear of EPS foam (Figure 7). As can be seen from the graph, it provides better handling strength within one hour as compared with the competitive adhesive.
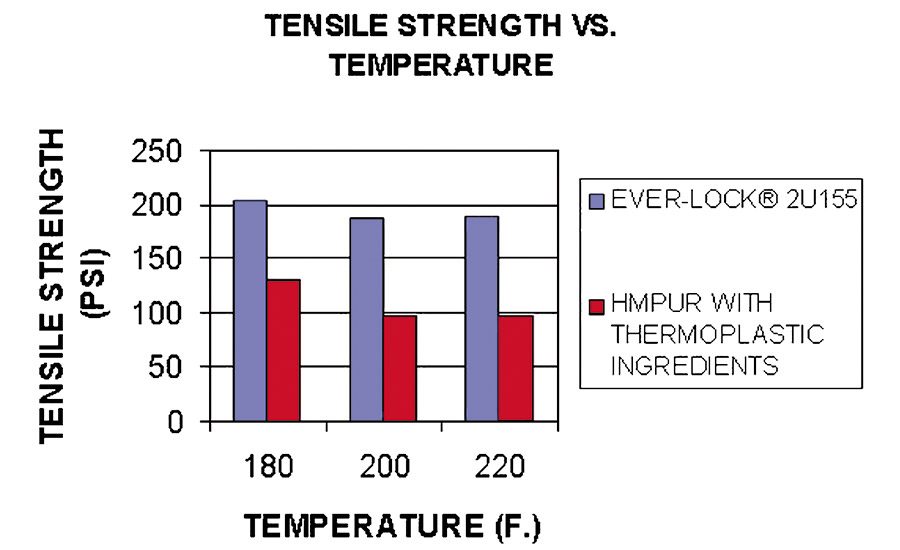
Another issue with adhesives for RV side walls as they are being used on vehicles is the potential for exposure to high temperatures during summer months, particularly in the Southwest United States. Dark areas of the side walls can easily reach temperatures of 180°F or higher when exposed to direct sunlight. Ever-Lock HMPUR adhesives are fully reactive, containing no blended thermoplastic material. This gives them substantially better high-temperature performance as compared to competitive HMPUR products, which incorporate thermoplastic materials (Figure 8).
HMPUR Adhesives for Textiles
There has been great interest in the use of HMPUR adhesives for textile applications in recent years2. Reichhold has a pilot coater that incorporates both a slot-head and a gravure-roll coater to support the development of these products and applications (Figure 9). Advantages of HMPUR adhesives for textile applications include:
- Low-viscosity Newtonian behavior, which allows for rapid machining and high line speeds at relatively low temperature. This means that heat-sensitive materials can be rapidly coated and laminated.
- Excellent hydrolysis resistance of specifically designed products allows HMPUR-bonded fabrics to be washed or autoclaved multiple times. This is important for medical and protective-apparel applications that require autoclaving for decontamination.
- Reactive flame retardants have now been incorporated directly into the backbone of the HMPUR adhesives. This has allowed textiles coated with these products to pass fire tests required by NFPA and some automotive standards. Since the fire-retardant materials are part of the chemical structure of the adhesive, there is no problem with blooming or extraction.
- Products have been developed for bonding very soft, low-surface-energy materials such as porous polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or Teflon and low-basis-weight polyurethane films for active-wear applications. Methods have been developed to produce breathable laminates using HMPUR adhesives.
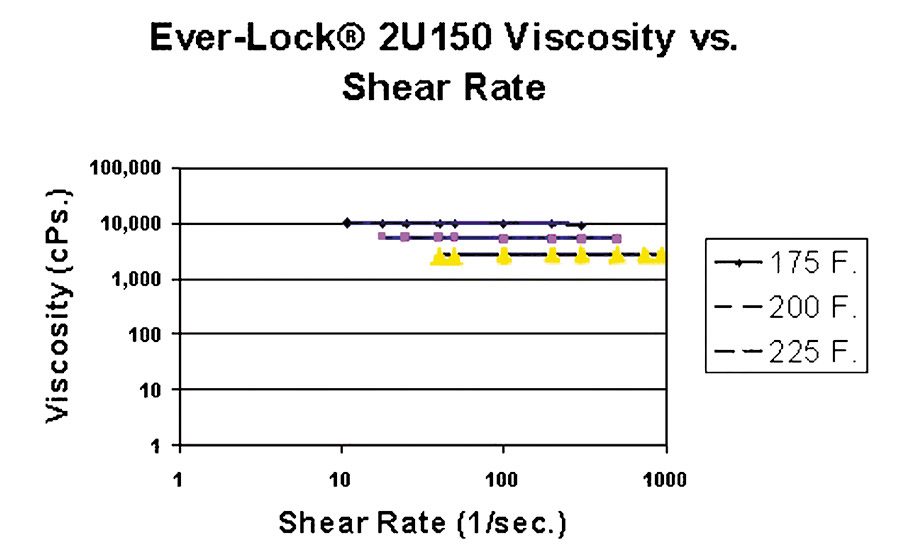
Ever-Lock 2U150 is an HMPUR adhesive with the low viscosity and Newtonian behavior needed for textile lamination at low temperatures. The graph in Figure 10a demonstrates its low viscosity and independence of shear rate over the temperature range of 175°F to 225°F.
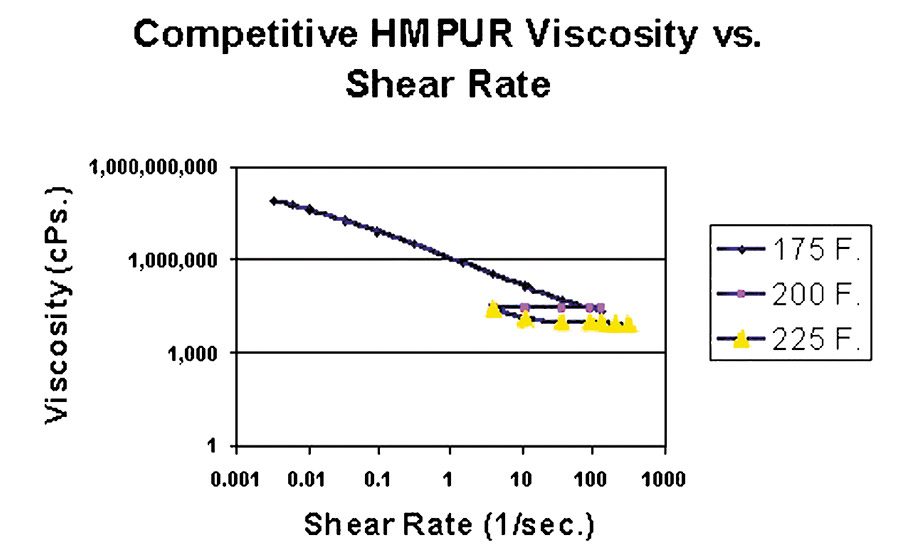
In contrast, the competitive product has both a higher viscosity and a large increase in viscosity at low shear rates at 175°F as shown in Figure 10b. The more-consistent lower viscosity of 2U150 allows it to run at lower temperatures and at higher line speeds than the competitive adhesive.
Ever-Lock 2U150 is also very resistant to hydrolysis in comparison to some older HMPUR products. By selecting specific raw materials, we have designed a product that will withstand continuous high-temperature autoclaving for up to 18 hours with minimal loss of properties. This is in marked contrast to another product, Ever-Lock 2U104, which is not designed for autoclaving and loses much of its tensile strength within six hours (Figure 11).
2U150 and similar products can be very effectively used to laminate textiles in applications requiring multiple autoclave cycles. If only washing is required, we have several other products that, while not as hydrolytically stable as 2U150, can work extremely well for large numbers of wash cycles.
Other Specific Applications for HMPUR Adhesives
Profile wrapping is a major growing application for HMPUR adhesives. This application makes use of the short set times and rapid green-strength development possible with proper formulation of HMPUR products. Some profile-wrapping applications involve the bonding of printed papers and plasticized vinyls onto MDF profiles. These wrapping materials require relatively low application temperatures and low viscosity of the HMPUR adhesive.
At the other extreme, wrapping high-pressure laminate (HPL) to PVC extrusions or wood profiles requires the application of high temperatures, very rapid green-strength development and short set times to wrap the stiff HPL material. Other customers need the non-yellowing adhesives that have been developed using HMDI and a patented catalyst system.
One recent development is a highly electrically conductive adhesive for applications requiring antistatic behavior or electrical conductivity. This has the potential of replacing other conductive adhesives such as epoxies or solvent-based adhesives with a product that has all the advantages of the HMPUR adhesives described in this article. In addition, HMPUR adhesives are being used in applications as diverse as bookbinding, automotive interiors and insulated garage doors.
Conclusions
As you have seen from the applications described in this article, HMPUR adhesives can be developed with a wide variety of properties to provide high performance for specific application requirements. These adhesives can provide highly efficient bonding operations with high line speed and efficient use of plant-floor space since their short set time and excellent green strength allow parts to be handled quickly. The fact that they are 100%-solids and require no drying or solvent handling makes them environmentally friendly and minimizes the use of heat energy for application. Reichhold has the capability of supplying these adhesives for many applications within our current product line. We also can rapidly develop HMPUR products for new applications.
This article is based on a presentation made at the Fall 2000 Adhesive and Sealant Council Convention in Minneapolis. Additional information on hot-melt polyurethane reactive adhesives discussed in this article is available from Reichhold, Inc., PO Box 13582, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709; call Timothy Moore, Marketing Manager, 800-213-4805; ext. 7194, fax 919-990-7886; e-mail timothy.moore@reichhold.com; or visit www.reichhold.com.