Novel Curing









An emerging technology may allow adhesives in opaque substrates to be cured by UV or visible light.
Adhesives and coatings cured by ultraviolet (UV) or visible light have become valuable tools in modern-day assembly operations, particularly in high-technology industries such as electronics and medical devices. Most UV adhesives are based on free radical polymerization systems with acrylate or methacrylate monomers, although other systems such as cationically cured cycloaliphatic epoxies, vinyl ethers, and oxetanes are known.
UV systems offer users the following advantages:
- Quick cure speed (often in seconds) leads to increased productivity
- Energy savings; requires a fraction of the power consumption of heat curing
- Fewer stresses and movement than in heat cure
- Less floor space due to small, compact curing systems
- Single component (no application of primers or mixing)
- Reduced work in process (assembly to pack measured in minutes)
- Safety (no hazardous solvents or other emissions)
Technological Innovation
A major obstacle limiting market penetration by UV systems has always been the necessity for the adhesive to be exposed to the incident light, thus requiring that one of the substrates be transparent. Most of the applications have therefore involved assemblies that include glass or transparent plastics, such as syringes and medical tubing.
New technology from Immunolight LLC uses proprietary materials called energy modulators to actually generate the light inside the adhesive bond (see Figure 1). The principle of this technology is that energy in the electromagnetic spectrum can be converted in wavelength or frequency by an energy modulator. The process for converting low-level energy (lower than UV) involves several steps:
- Low-level energy (radio frequency, microwave, infrared, etc.) is used for excitation
- The modulator absorbs the low-level energy and up-converts it
- Photons are created to do work
- This process is an energy up-conversion, and it is inherently not highly efficient
- Converting high-level energy, on the other hand, is slightly different:
- X-ray is used to excite an excitation energy modulator
- The modulator absorbs the X-ray energy and emits energy at a different wavelength
- Photons are created to do work
- This process is called down-conversion and is more efficient
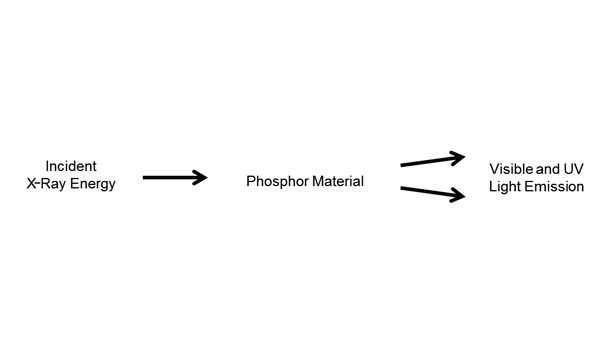
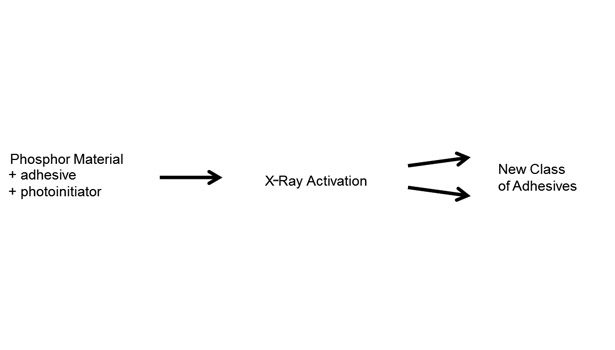
In practice, the optimum system uses particles (from nanometers to micrometers in size) having phosphorescence as an attribute. These particles act as the energy modulators, and they are activated by low-energy X-rays (see Figure 2). Thus, a conventional UV adhesive based on acrylates or methacrylates and containing a photoinitiator can be activated inside an assembled bond by exposure to the X-ray source, which inherently penetrates deeply inside both opaque and non-opaque materials alike (see Figure 3).
It should be noted that this technology is quite different from high-energy systems such as electron beam or straight X-ray curing of adhesives. This technology uses low-energy X-ray systems of 100-300 kVp, which have become common in inspection systems in the semiconductor and metals industries.
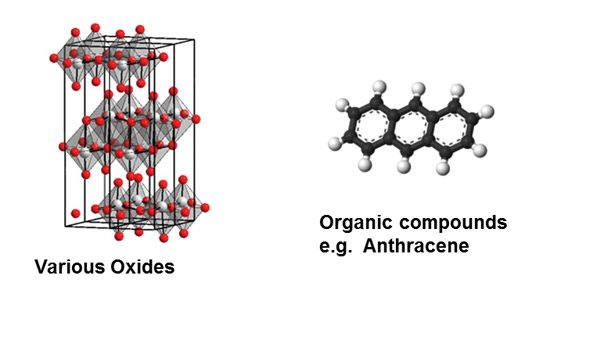
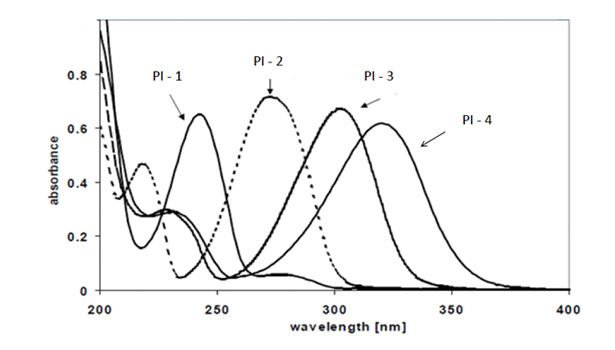
Examples of the inorganic and organic phosphors that can be used can be seen in Figure 4. Figure 5 shows the absorption spectra of four commonly used commercial photoinitiators, and Figure 6 shows the emissions from typical phosphors used in this technology. In fact, the phosphors can generate energy all the way from short-wave UV though the visible spectrum of blue to red (see Figure 7).
Multiple Advantages
Some of the energy-modulating materials emit UV or light energy for 10-100 seconds after being irradiated by X-ray energy. These energy-modulating compounds are now commercially available in large scale, are non-hazardous and have good miscibility into various resins. They can be added to standard UV-curable adhesive chemistries or can form a completely new class of adhesives.
The benefits of this technology include:
- Curing without “line-of-site” UV activation, including opaque materials (the bond line where adhesion takes place is internal to the structures to be bonded)
- Curing without depth of penetration limitation (the bond line can be deep inside materials without compromising the cure kinetics)
- Curing without thermal expansion mismatch (provides the ability to bond at room temperature and avoid compressive and tensile stresses at the bond line)
- Curing adhesive selectively (the adhesive only cures where it has an energy-converting particle)
- Curing “shaded” or “shadow” areas (avoids the necessity for secondary cure systems in filled adhesives or complex coating applications)
- Concurrent curing and inspection using X-ray
Feasibility has been demonstrated in free-radically polymerized systems, including acrylates and acrylate or methacrylate-functionalized silicones. These adhesives can be cured in typically 18-30 seconds through bond gaps of over 30 mils. Cationic photoinitiators can also be used to cure cycloaliphatic epoxy adhesives (and potentially vinyl ethers and oxetanes).
Potential applications for this technology include both high value-added and high-volume applications in the following industries:
- Computing, display and mobile devices
- Medical devices, medical electronics and micro-fluidic devices and pumps
- Opto-electronics (various fiber attachments)
- Semiconductor stacking
- Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS)
- Automotive and aerospace composites
- The following electronic application examples have been reduced to practice:
- Chip on flex/PEC, polyimide, ABS
- Chip on board/multi-layered FR4 and ceramic
- Die to wafer/silicon (Si) and gallium arsenide (GaAs)
- Wafer to wafer/Si and GaAs
About Immunolight, LLC
Immunolight, LLC has a strong patent portfolio with multiple applications pending and additional filings in development, encompassing chemistry, device making, methods, and apparatus. The company is actively seeking strategic partnerships for deploying the technology to the marketplace for specific applications in individual market segments. Interested partners should contact Harold Walder, president, at hwalder1@gmail.com.
About the Author
Dave Dunn, Ph.D., is president of FLD Enterprises, a technical and management consultancy specializing in the adhesives and sealants industry (www.fldenterprises.com). A former vice president and director of Loctite Corp., he is a contributing editor for ASI and writes the monthly Q&A column called “Ask Dr. Dave.”
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!












