Vinylesters for PSAs








Due to the many advantages they offer over other technologies, waterborne, acrylic pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) have developed a strong position over the years. Further improvement of their water resistance properties and adhesion to low-surface-energy substrates could allow increased growth of these technologies in some specialty label areas, such as labeling for beverages, hard and flexible plastic packages, personal and home care, oil and industrial chemical, and pharmaceutical and health care.
Many specialty tape applications can be found in the electronics, construction and automotive industries. Despite development efforts, however, existing waterborne PSA technologies lack the appropriate cohesion/adhesion balance required for high bond strength, heat and UV resistance performance at an acceptable cost level.
VINYLESTERS
A line of vinylesters in a homopolymer Tg range from 70°C down to -36°C is available.* These monomers are highly hydrophobic and display a great hydrolytic resistance, resulting from the alkyl groups (see Figure 1).
In decorative paints and protective coatings, hydrophobization of the polymer backbone with the vinylester monomers is known to enhance the coating’s water and alkaline resistance and, more generally, outdoor durability. In woodworking, the monomers allow for the manufacture of high-performing wood adhesives (D3 and D4 types).
Recent developments with these vinylesters have shown the benefits of using hydrophobic vinyl esters as building blocks for waterborne PSAs, either by directly modifying the acrylic polymer backbone, or by designing new polymers on the basis of the vinyl ester chemistry. The modification of a waterborne acrylic PSA with the vinyl ester monomers has proven to be straightforward, allowing the polymerization process and general characteristics of the latex to remain unaffected. The introduction of the vinyl ester monomers in the backbone of an acrylic polymer has a remarkable effect on the shear holding power of the PSA. Moreover, these PSAs exhibit a good level of adhesion and tack. It can therefore be concluded that the presence of the hydrophobic vinyl ester monomer allows for a substantial improvement of the adhesion/cohesion balance consistent with solvent-based acrylic PSAs.
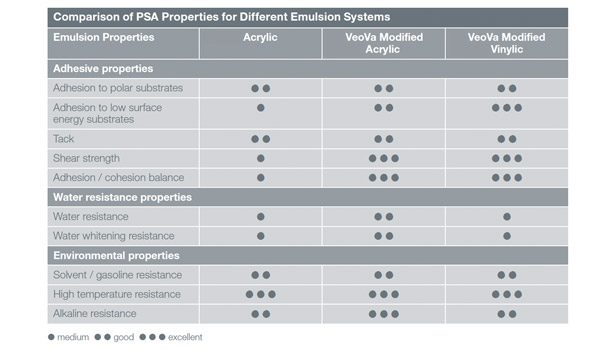
The introduction of these co-monomers also has a strong effect on the chemical and alkaline resistance, as well as the water resistance (including humidity resistance, water whitening and water vapor permeability) of the resulting pressure-sensitive product. Table 1 provides a comparison of PSA properties for different emulsion systems and shows that the monomers enable the development of vinyl-modified acrylic PSA and modified vinylic PSA formulations.
* VeoVa™ vinylesters, manufactured and supplied by Momentive.
REAL-WORLD BENEFITS
Water resistance in PSAs is not only needed to maintain performance levels in applications that can be exposed to outdoor conditions, but it is also necessary in applications where whitening resistance is needed in order to preserve good clarity and aesthetics of the finished goods. In warm and humid regions, PSA-coated rolls may be stored for a prolonged period. It is critical to maintain the initial performance of the PSA under such conditions. Under the conditions of an accelerated aging test (seven days under 90% relative humidity and 35°C), the vinylester-modified PSAs retain almost 80% of their initial adhesion value, as well as their cohesive strength.
In addition, different specialty label applications require a PSA to show good resistance against water whitening. Figure 2 demonstrates the outstanding whitening resistance obtained for the vinylester-modified PSA after 48 hours of direct contact with water.
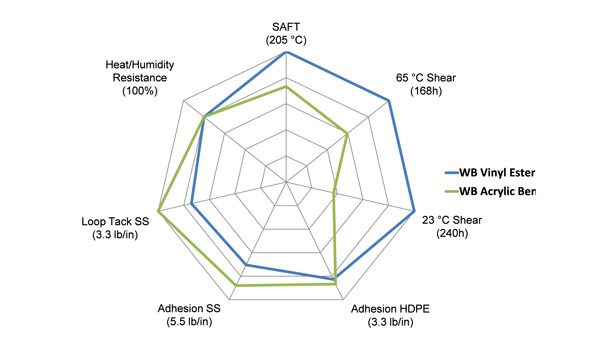
The addition of tackifier dispersion to a polymer binder is quite common in the PSA industry, as this typically enables the PSA producer to increase the tackiness and improve the adhesion of the material onto low-surface-energy substrates. Yet those additives negatively impact the cohesive strength and the water resistance of the PSA. Interestingly, the modified PSAs are able to maintain both their excellent cohesive strength and water resistance, including the very good water whitening behavior, despite the addition of a standard tackifier dispersion. Vinylester-modified acrylic PSAs can also be developed with high adhesion levels on stainless steel and high-density polyethylene (HDPE) showing high shear strength (see Figure 3).
In light of the enhancement of PSA properties obtained when modifying an acrylic polymer with the hydrophobic vinyl esters, and thanks to the recent development of softer hydrophobic vinylester,** a new class of PSA materials has been developed based primarily on vinylester monomers. This new approach allows for the development of new PSA materials possibly showing a new level of performance, along with the ability to use other monomers than acrylics. These new PSAs show high shear resistance coupled with improved adhesion to low surface energy plastics, such as HDPE or Teflon. Although the adhesion level is lower on Teflon compared to HDPE, the value obtained is still significant; most waterborne, acrylic PSAs tend to show adhesion levels in the range of 0.3 lb/in.
**VeoVa™ EH, Tg = -36°C
A VERSATILE TOOL
On the basis of this performance profile, such material appears as an interesting candidate for specialty tape applications where solvent-borne acrylic PSAs are still predominantly used due to their high peel on multiple substrates, good tackiness and high shear strength in combination with good chemical and heat resistance. The stability of the vinylester PSA-based tapes against UV, elevated temperatures and high humidity was also assessed.
Figure 4 presents a summary of the current findings. It shows that these vinylester-based PSAs can combine a good adhesion/cohesion balance, even on LSE substrates, with good heat, humidity and chemical resistance. The modification of waterborne acrylic PSAs by hydrophobic vinylesters may therefore be considered as a valuable option to reduce the performance gap between waterborne and solventborne acrylic PSAs.
These vinylester monomers present a versatile tool to enhance the performance of waterborne acrylic PSAs and even allow for PSAs with unique performance attributes that are purely based on vinylesters. Optimum results are typically obtained through a collaboration between the monomer supplier, the resin supplier and the PSA producer.
For more information, contact Egbert Klaassen, Global Marketing Director Versatics, at (49) 0173-6577822 or egbert.klaassen@momentive.com.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!









