Market Trends: Bioadhesives Fill the Gaps
Bioadhesives can address several unmet needs in key industries like healthcare and pulp and paper.



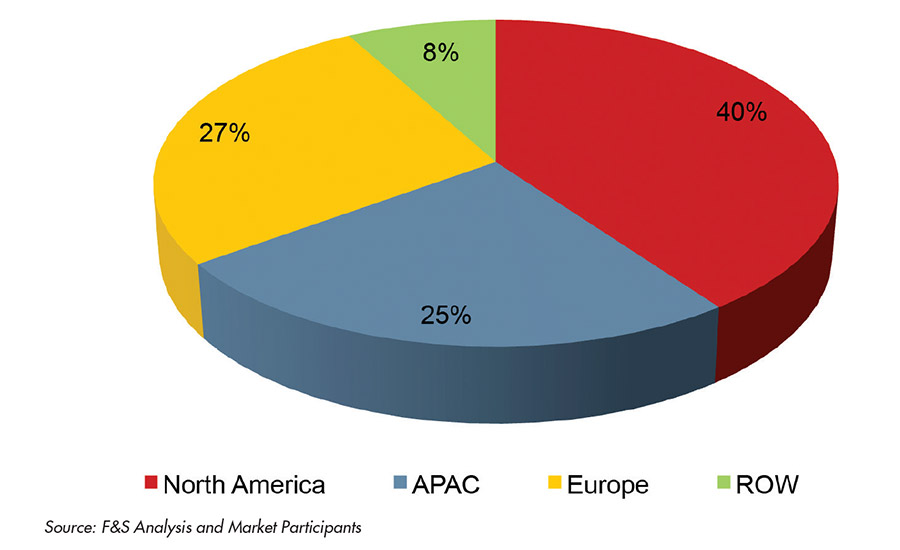
Vast technological capabilities and the addition of more viable solutions have gradually reduced unmet needs across several industries. Many bioadhesive vendors are currently licensing new solutions to product developers that are looking to strengthen their portfolios—and market positions.
According to “Impact of Bioadhesives in Key Sectors,” a recent report from Frost & Sullivan, animal glues and starch- and gum-based bioadhesives have found uses in key sectors, fulfilling the need for biocompatibility, eco-friendliness, and adhesion. The study covers the healthcare, personal care, and paper and pulp industries.
“Bioadhesives have increasingly filled gaps that have developed due to the absence of natural substances suitable for the healthcare, personal care, and pulp and paper industries,” said Sanchari Chatterjee, technical insights research analyst. “Advanced adhesive functionalities for drug delivery systems as well as bio-compatibility and tissue friendliness for wound-closure applications have spurred use of bioadhesives. Another major business accelerator of the bioadhesive market is the global inclination toward bio-based materials and reduced use of synthetic adhesives.”
While bioadhesives are generally as competent as synthetic adhesives, a major drawback is limited shelf life. Particularly in healthcare, the need to reduce operating costs strengthens demand for products that last longer in internal tissues. Moreover, shelf-life requirements for individual sectors differ; hence, research projects must focus on blending polymers to derive the most capable products.
“Lack of skilled resources is another challenge, as integration of materials and bio-sciences and the invention of new polymeric products creates a disproportionate base of knowledgeable personnel,” Chatterjee said. “Establishing training facilities will be key for greater product development at the laboratory scale and commercialization at a global scale.”
For more information, visit www.frost.com/d61b.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!