Sustainability
Scientists often look to nature to find alternative ways to current methods, and researchers in northeast India are doing just that.
Read More
‘Tis the Season for Children’s Safety
Some towns around the country have already began the banning of these products and looking for alternatives.
December 6, 2017
Global Bioadhesives Market Continues to Jump 13%
A range of applications reportedly represent the key factor driving the global bioadhesive market.
November 28, 2017
Market Trends
Environmental Coatings Consumption Continues to Rise
Many developed economies are now reportedly using a significant percentage of “green” technologies
November 24, 2017
H.B. Fuller Facility Receives LEED® Gold Certification
The new facility is one of only three facilities in the country to receive the Gold certification.
November 16, 2017
Artecola Opens Plant in Colombia
The plant supplies to the markets of Peru, Ecuador, Panamá, Bolívia, Caribe and Colombia itself, among other countries.
November 16, 2017
AGC Chemicals Celebrates 100 Years
Asahi Glass began the chemical business in 1917 to produce soda ash, a raw material in flat glass.
November 13, 2017
The Future Is in Sustainability and Safety
To remain competitive, suppliers must deliver innovations that enable formulators to develop products that satisfy consumer demand.
November 1, 2017
Advancing Adhesives
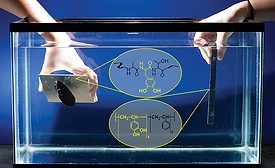
Underwater Bonding
A new “biomimetic” glue can provide high-strength bonding under water.
November 1, 2017
Keep the info flowing with our eNewsletters!
Get the latest industry updates tailored your way.
JOIN TODAY!Copyright ©2024. All Rights Reserved BNP Media.
Design, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing