Columns
Which articles have been most useful to you, and which ones did you skip over?
Read More
Ask Dr. Dave: April 2013
Dave Dunn shares details regarding UV adhesives/coatings for a medical device assembly.
April 1, 2013
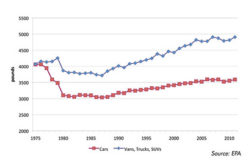
Strategic Solutions: Fuel Economy Standards and the Adhesives Market
Robust demand is expected to offer opportunities for adhesives.
March 1, 2013
Editor’s Memo: Materials Handbook
Welcome to our annual Raw Materials, Chemicals, Polymers and Additives Handbook.
March 1, 2013
Ask Dr. Dave: February 2013
Dr. Dave answers a question about the recycling of adhesives and sustainability in the adhesives industry.
February 1, 2013
Regulatory Review: Categorical Considerations for VOC Regulation
Some products that are considered to be coatings may not lie within the architectural coatings rule, but may instead cross over to adhesives and sealants rules—or even others.
February 1, 2013
Editor’s Memo: Electronics Applications
CEA's 2013 International CES event was held last month; Electronics West will be held this month.
February 1, 2013
Keep the info flowing with our eNewsletters!
Get the latest industry updates tailored your way.
JOIN TODAY!Copyright ©2024. All Rights Reserved BNP Media.
Design, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing