Market Trends: China Is a Hot-Melt Adhesives Hot Spot
China's domestic market for hot-melt adhesives was around $1.62 billion in 2014, an increase of 11% from 2013.



From the construction of King Tut’s tomb during the time of the pharaohs, to ensuring the airtight bonding of planks while shipbuilding by the Romans, adhesives have served numerous applications—and made their mark on history. With the invention of thermoplastic adhesives, more commonly known as hot-melt adhesives (HMAs) occurring only 70 years ago by Procter and Gamble, the industry has undergone large transformations from its roots in ancient civilization. In the Chinese domestic marketplace, recent economic trends, consumer behavior, and developments to product technology and delivery systems have all merged to shape the hot-melt adhesives market.
Hot-melt adhesives are composed of three main components: a high-molecular-weight polymer that provides the adhesives’ main structure and mechanical properties, a resin/tackifier that provides wetting and adhesion properties, and a plasticizer (or wax) that controls viscosity. The defining component of the hot melt and the basis by which it is segmented is the polymer, the most commonly used being polyamides, polyesters, ethylene-vinyl acetates, polyurethanes, and various block copolymers.
Unlike their water- or solvent-based counterparts, hot melts require no drying or curing; they are applied in their molten state and begin bonding almost immediately after application. In packaging, bookbinding, nonwovens, footwear, and other markets, this gives hot-melt adhesives the distinct advantage of very fast processing times.
Market Overview
GCiS China Strategic Research estimates that China’s domestic market for hot-melt adhesives was worth around RMB 10,066 million in 2014 (~ $1.62 billion), up by 11% from 2013. An additional RMB 1,183 million (~ $193,000) was generated in exports. While EVA, SIS/SBS, PA, PES, TPU and PUR hot-melt adhesives all find extensive use in the Chinese marketplace, EVA and SIS/SBS hot melts are the chief product segments, together making up 75% of the market share.
Over 185 suppliers are active in China’s HMA industry, a large majority of which are privately owned Chinese companies. Of these, 54% of total revenues are earned by 18 large-sized suppliers with more than RMB 100 million (~ $16 million) target revenues. The remaining 46% is earned by 132 small-sized companies with revenues of less than RMB 50 million (~ $8 million), and 35 medium-sized companies with revenues of RMB 50-100 million (~ $8-16 million). Leading suppliers in the Chinese market include Henkel, H.B. Fuller, Bostik, Tex Year Fine Chemical, Zhongshan CherngTay, and 3M China.
Key End User Industries
Total 2014 HMA growth in China was 11%, representing a small pullback from the breakneck growth speed seen over the previous few years. This was due in large part to a shrinking export market and overall market slowdown causing sluggish growth in key downstream industries. As downstream industry orientates itself away from exports and toward internal demand, industries such as bookbinding and footwear have been negatively impacted, while others have been reaping benefits. Industry observers have hailed the packaging and hygiene products sectors as hot-melt adhesives’ engines for growth in upcoming years, describing them as “currently in phases of rapid development which have not yet crested.”
Innovation in this field is multi-purpose and often seeks to benefit the customer by reducing dosage, waste, maintenance on machinery, and customer downtime, and by increasing production speed. In the North American market, smart packaging, which features moisture control and status indication, has been on the rise. In China, however, product standards and expectations are less rigorous, and domestic suppliers are trying to switch from traditional “heated tank” dispensing systems, which can contaminate and char the hot melt, to more modern equipment. Basic hot melts based on EVA or SBS/SIS technology within packaging have lost share to products like the more specialized EVA hot melts, which can be applied at lower temperatures. Recent developments in industry make use of new polymers and lower content of scarcer resources.
Packaging
The most important market for hot-melt adhesives in China has long been packaging. In particular, the production of tapes and labels has been experiencing immense growth. An increase in Chinese purchasing power, combined with consumption trends, has also lead to more varied, complex, single-serve pack sizes, which has also been positively fueling the industry. Another contributing factor to latent demand for hot melts within packaging were the traditionally low levels of automation, which caused many packaging producers to use alternate forms of adhesive.
Hygiene
The hygiene products industry has likewise been bolstered by increased consumption in the domestic market, and will be minimally impacted by the downturn. The hygiene products industry uses primarily SBS/SIS-type hot melts for their ability to retain flexibility and elasticity at low temperatures. This provides the stretch required by many of the final products, such as the elastic waistband on diapers.
The trend of recent years toward top-quality goods is continuing, whereby the product value of big multi-national companies is unbeatable. This has prompted increased foreign investment into China from large multi-nationals, such as Kimberly-Clark and Unicharm. While this speaks well for the anticipated growth of the hygiene products market in China, it has also put extreme pressure on mid-sized companies to increase competitiveness to find their own piece of the market, and has all but driven out small-sized businesses.
Electronics
Though electronics make up a comparatively small share of overall HMA revenues, it saw the highest growth in 2014 of all end-user industries. It is projected to continue to grow at the fastest rate moving forward, due to a very strong export market and booming internal demand for personal electronics devices. Telecommunication equipment, especially for cell phones, household audio and video, and electronic components, all saw very high growth in 2014. High-performance hot melts (e.g., specialized EVA and organic-silicon hot melts) with temperature and oxidation resistance are highly sought after, serving to increase their share of the market.
Contributing to growth within these markets are recent regulatory incentives promoting the use of environmentally friendly products, beginning in the 12th five-year plan. In contrast to waterborne or solvent-based adhesives, hot-melt adhesives have no volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and are much more environmentally friendly in terms of manufacturing and disposal. As a result, many electronics manufacturers are choosing hot-melt adhesives, thus strengthening the hot-melt adhesive scope of influence within this industry.
Domestic and Foreign Rivalry
A key trend in the hot-melt adhesive market is the movement toward higher quality products. HMA is a large determinant to the end-product’s overall quality, while typically only incurring only a small part of the overall cost. Accordingly, as end-products continue to be realized further down the value chain, customers are beginning to choose higher-end products. The ongoing shift toward higher quality adhesives has brought about a surplus of low-end goods and intense competition in that area of the market. Consequently, it has encouraged many mid- and low-level suppliers to invest more heavily in R&D in the hope of being able to penetrate the more lucrative high-end market.
This trend has mainly benefited foreign suppliers, which as a group hold a 38% market share. Foreign suppliers, typically Chinese branches of major multinationals, purport strong year-on-year growth; despite this trend, domestic suppliers have been gaining more market share. This trend is expected to continue, as the sheer growth in this market is often being filled by domestic companies rather than by foreign ones.
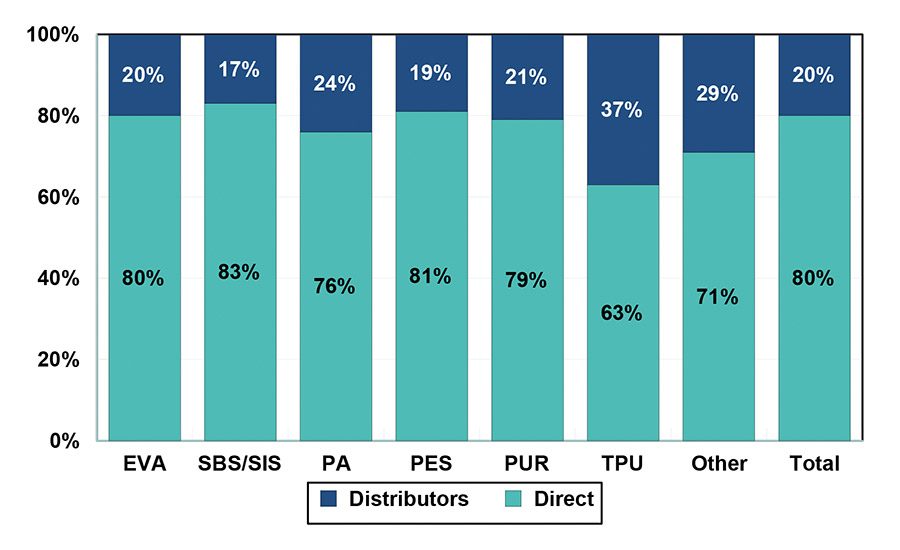
Foreign companies will continue to dominate the more lucrative high-end market, primarily owing to superior R&D, as well as supply chain efficiencies that allow for easier access to high-quality raw materials. Due to the comparatively high demand within the domestic market in China, exports will continue to shrink as a proportion of overall revenues. Lastly, as connections become more established, the entire market is trending toward direct sales, rather than using distributors. This is observed even more acutely among foreign suppliers, who historically relied more heavily on distributor companies.
For more information, visit www.gcis.com.cn.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!







